Baxter Unveils Olimel 7.6% High Protein Nutrition Formulation at the 2018 ESPEN Congress
Highest protein and lowest glucose formulation among Parenteral Nutrition (PN) products, available in a standardized, triple-chamber bag1,2,3,4
New PN formulation will help meet needs of high stress patients who require more protein and are often impacted by hyperglycemia
OLIMEL 7.6% is the latest addition to Baxter’s olive oil-based parenteral nutrition portfolio
Currently approved in Canada, Baxter plans a global launch in 2019
Deerfield, Ill. -
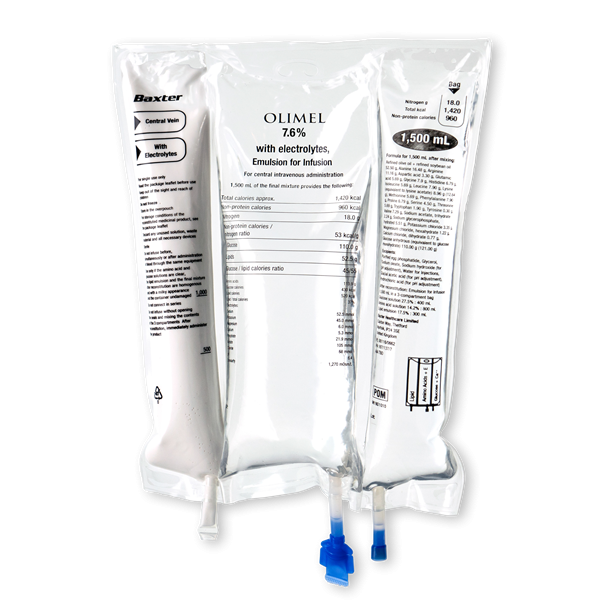
Baxter International Inc. (NYSE: BAX), a global leader in clinical nutrition, is showcasing OLIMEL 7.6%, the latest addition to the company’s olive oil-based parenteral nutrition portfolio, at the 40th Congress of the European Society of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN), taking place from September 1 to 4. Currently approved in Canada, OLIMEL 7.6% is a ready-to-use solution designed to meet the needs of high stress patients by combining the highest protein with the lowest glucose formulation available in a standardized, triple-chamber bag.
Critically ill patients and those who have major surgery may require parenteral nutrition, which may be necessary when a patient cannot get adequate nutrients orally or through tube feeding. Most of these patients receive less than half of the protein that is recommended for more than 10 days in the ICU5. While recent studies show that higher protein treatments were associated with lower mortality rates in the ICU6,7 giving patients more protein with ready-to-use products can have the unintended consequence of increasing their intake of glucose and potentially lead to overfeeding.
“Ready-to-use products containing higher protein may help patients reach their protein targets, and help them ensure they have the best chance to survive and recover their quality of life after an ICU stay”, explained Paul Wischmeyer, M.D., professor of Anesthesiology and Surgery at Duke University School of Medicine. Dr. Wischmeyer is leading several presentations at ESPEN, including a webinar on the importance of muscle mass/lean mass and nutrition intervention in the acute care setting and ICU.
Baxter’s latest OLIMEL 7.6% formulation provides clinicians new options for treating critically-ill patients, as it includes:
- 76g of protein (amino acid) per liter, designed to deliver protein targets in lower fluid volumes.
- Only 73g of glucose per liter, which helps reduce the risk of hyperglycemia.
- Olive oil-based lipid emulsions that may preserve immune function8,9,10,11,12
“With the addition of the OLIMEL 7.6% formulation, we now offer a comprehensive PN portfolio to meet the unique needs of high stress patients,” said Jorge Vasseur, general manager of Baxter’s Clinical Nutrition business. “Baxter is focused on advancing innovation for patients across the hospital and ensuring clinicians have ready access to nutrition solutions that are designed to help patients recover and regain their health.”
The use of high protein regimens and olive oil-based lipid emulsions are supported by guidelines from both ESPEN and the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (ASPEN).
The new OLIMEL formulation is expected to launch globally in 2019. For more information on OLIMEL, please visit: https://www.baxter.com/healthcare-professionals/nutritional-care/olimel-portfolio-nutritional-care.
About Baxter's Global Clinical Nutrition Business
Baxter has been assisting clinicians in treating patients' diverse nutrient needs since the 1940s, when the company first introduced liquid proteins in the form of amino acids. Since then, Baxter has continued to advance nutritional therapy. As an example, Baxter pioneered the world's first "triple-chamber system" internationally for IV nutrition, which provides many of the essential ingredients of balanced nutrition – protein, carbohydrates, lipids and electrolytes in a single container -- simplifying the preparation of parenteral nutrition for patients.
Today, Baxter provides one of the broadest parenteral nutrition portfolios globally, which includes premix IV solutions, vitamins and lipids, as well as pharmacy workflow management, labeling and compounding technology. Baxter’s lipid emulsions are available globally in multi-chamber, ready-to-use solutions, and single solution bags that can be added to a compounded or premixed bag to ensure clinicians can prescribe the best well-balanced therapy for their individual patients.
About Baxter
Every day, millions of patients and caregivers rely on Baxter’s leading portfolio of critical care, nutrition, renal, hospital and surgical products. For more than 85 years, we’ve been operating at the critical intersection where innovations that save and sustain lives meet the healthcare providers that make it happen. With products, technologies and therapies available in more than 100 countries, Baxter’s employees worldwide are now building upon the company’s rich heritage of medical breakthroughs to advance the next generation of transformative healthcare innovations. To learn more, visit www.baxter.com and follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn and Facebook.
* Important Safety/Risk Information for OLIMEL 7.6%
Therapeutic indications: OLIMEL (amino acids WITH electrolytes, dextrose, lipids) or (amino acids, dextrose, lipids) is indicated for parenteral nutrition for adults when oral or enteral nutrition is impossible, insufficient or contraindicated. Geriatrics: There are no known differences in safety and effectiveness of parenteral nutrition formulations in the adult population based upon age. Pediatrics: There have been no studies performed in the pediatric population.
Contraindications: The use of OLIMEL is contra-indicated in the following populations/situations: Known hypersensitivity to egg, soybean products, olive products or any of the active substances, excipients, or components of the container. Known allergy to corn or corn products since the products contain corn-derived dextrose, patients with acute renal failure and without undergoing renal replacement therapy, patients with severe liver failure or hepatic coma, congenital abnormalities of amino acid metabolism, severe hyperlipidemia or severe disorders of lipid metabolism characterized by hypertriglyceridemia, hypertriglyceridemia-associated acute pancreatitis, severe hyperglycemia. Additional contraindications specific to OLIMEL formulations with electrolytes: hyperkalemia, hypercalcaemia, hyperphosphatemia, hypernatremia, hypermagnesemia, ceftriaxone must not be administered simultaneously with intravenous calcium-containing solutions, including OLIMEL, through the same infusion line (e.g. via Y-site) because of the risk of precipitation of ceftriaxone-calcium salt.
This release includes forward-looking statements concerning current and existing OLIMEL product formulations (including OLIMEL 7.6%). Those statements include potential benefits associated with the use of these products and anticipated market launch dates (for future OLIMEL formulations). The statements are based on assumptions about many important factors, including the following, which could cause actual results to differ materially from those in the forward-looking statements: satisfaction of regulatory and other requirements; actions of regulatory bodies and other governmental authorities; product quality, manufacturing or supply, or patient safety issues; changes in law and regulations; and other risks identified in Baxter's most recent filing on Form 10-K and other SEC filings, all of which are available on Baxter's website. Baxter does not undertake to update its forward-looking statements.
Olimel and Baxter are registered trademarks of Baxter International Inc.
1 OLIMEL N12 SmPC, 2017
2 SmofKabiven SmPC, 2017.
3 NutriFlex SmPC, 2015
4 Trimix HP SmPC, 2017.
5 Hoffer and Bistrian. Am J Clin Nutr 2012;96:591–600.
6 Elke G et al. Critical Care 2014;18:R29.
7 Allingstrup Clinical Nutrition 2012;32: 460=18.
8 Jia Nutrition Journal 2015;14-119.
9 Calder PC, et al. Intensive Care Med 2010;36:735-49.
10 Granato D, et al. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 2000;24:113-8.
11 Olthof E, et al. Clin Nutr 2013;32:643-649. 4. Pontes-Arruda A, Clin Nutr Suppl 2009;4:19-23. 5.
12 Waitzberg DL, et al. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 2006;30:351-67.